neoplasia in cats bladder
What is a urinary tract tumor. The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma1 2 Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most prevalent lower urinary tract cancer in dogs and considerable information regarding TCC is available for dogs including.
Urinary Tract Tumors Vca Animal Hospitals
Renal neoplasia can originate in the kidney primary or spread or metastasize to the kidney from another site secondary.

. Neoplasia and the kidneys Renal lymphoma is the most common renal tumor in cats and often presents with sudden onset of poor kidney function including acute kidney injury 2. When tumors appear in the urinary tract of cats the cells that line the urinary tract are affected. The exact cause of tcc is usually not known but in general canine tcc results from a combination of.
In general TCC is an aggressive highly invasive. There are several types of bladder tumours in cats transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most common other types include benign mesenchymal tumours squamous cell carcinoma rhabdomyosarcoma and lymphoma. Study sets textbooks questions.
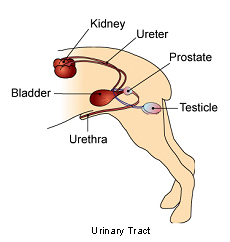
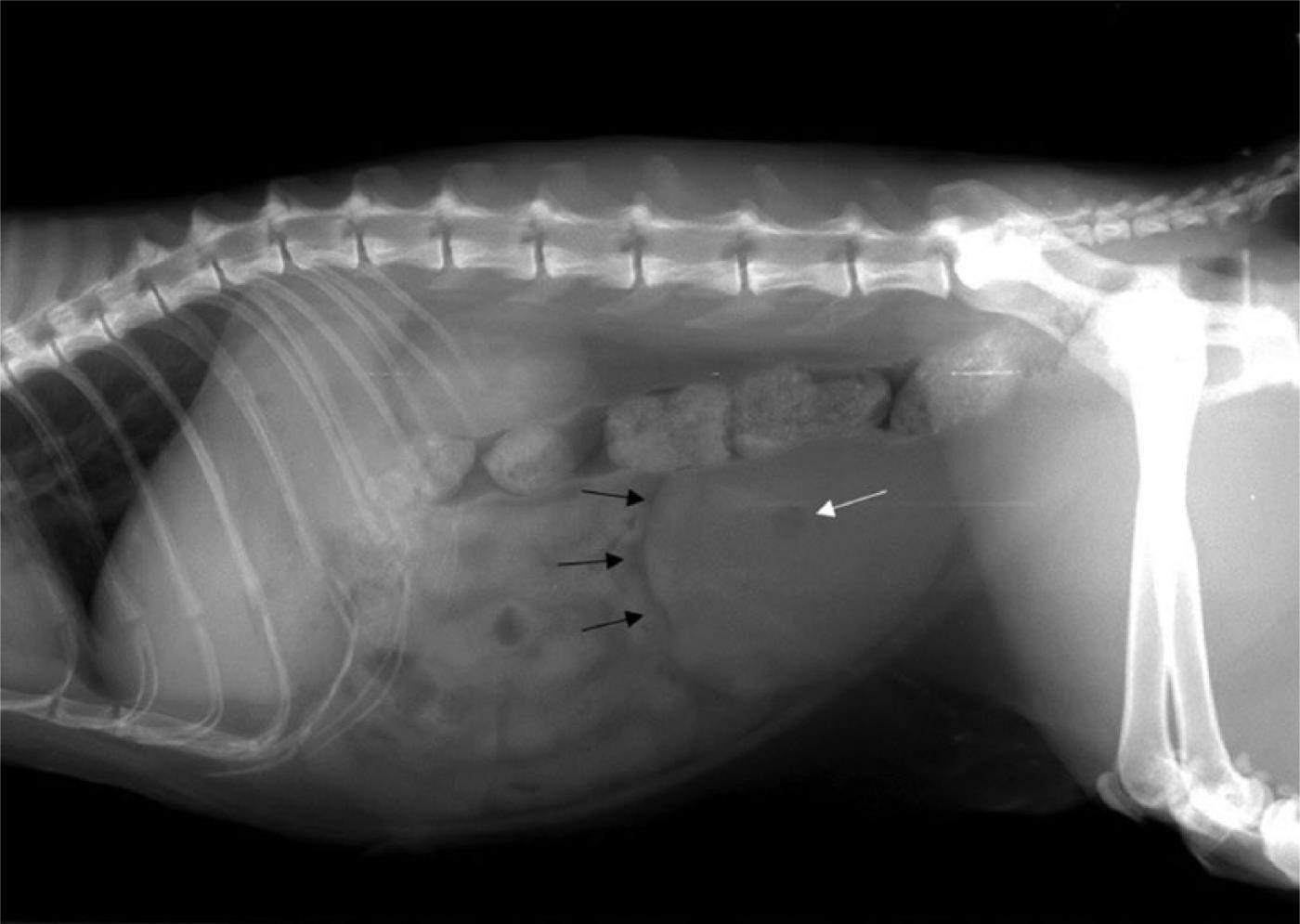
A tumor of the urinary tract could involve the kidneys ureters the tube that carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder urinary bladder prostate gland in males and urethra the tube that carries urine. 2 of all canine tumors. Euthanasia was performed and necropsy revealed an extensive nodular thickening of the entire urinary bladder wall.
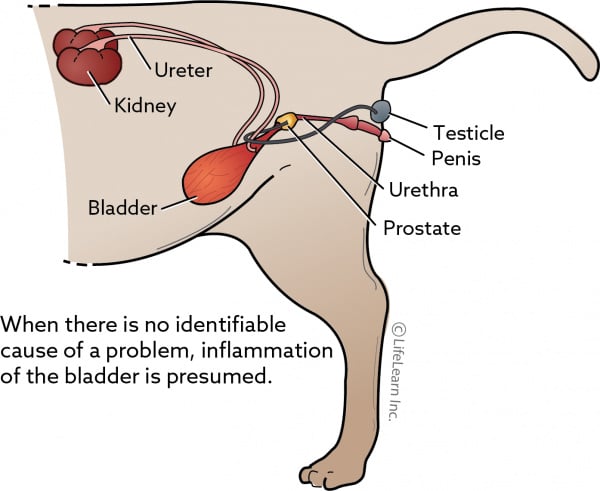
Depending on the location of the tumor the cat may or may not present symptoms. Much less common than in cats May be uni or bilateral Often no associated clinical signs. Bacteruria pyuria and positive urine cultures are common in cats.
Neoplasms of the canine and feline urinary bladder are diagnostic and therapeutic challenges to the veterinary clinician. Chronic urinary tract infection UTI. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Most renal tumors are seen in middle aged to older dogs and cats. A bladder tumor may be located in different areas of the bladder. However due to delays in diagnosis.
The cat was reported to be incontinent and treatment was declined by the owners. What is the treatment for renal lymphoma. Surgical resection by partial segmental resection is the treatment of choice.
Very rare. The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites. Nephroblastomas rapidly developing malignant tumors are seen in younger animals.
Bacterial in 65-75 cases. The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma. Epithelial tumors in particular TCC are the most common tumors of the urinary bladder and account for up to 92 of feline bladder tumors Other urinary bladder tumors include SCC ADC rhabdomyosarcoma FSA CSA leiomyosarcoma HSA chemodectoma and benign tumors such as leiomyoma and fibroma.
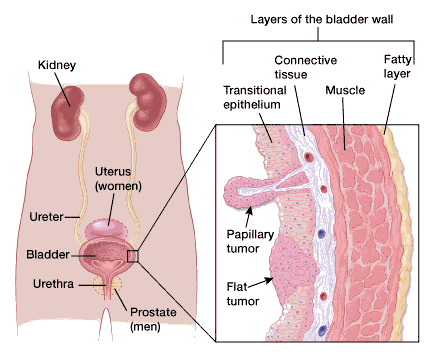
Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a malignant aggressive and metastasizing spreading cancer arising from the transitional epithelium the highly stretchable lining of the urinary tract system of the kidney ureters the tubes that carry fluid from the kidneys to the bladder urinary bladder. The occurrence of bladder cancer is more common in female cats. In cats the most common sites of metastases are abdominal serosa lymph nodes lung and liver.
Lower Urinary Tract Neoplasia 1. Neoplasms of the ureters bladder and urethra are uncommon in dogs and rare in cats. When tumors appear in the urinary tract of cats the cells that line the urinary tract are affected.
Chronic urinary tract infection UTI Cystitis. Feline leukemia virus associated lymphoma seems to be declining but possibly 14 to 50 of cats affected by lymphosarcoma are FeLV positive 3. Bloody urine Urethral obstruction causing an inability to urinate Pain upon palpation of the back or pelvic regions Weakness Exercise intolerance Polydipsia Polyuria with only a small.
The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites. Transitional Cell Carcinomas Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a prevalent type of bladder cancer in cats and more cats get diagnosed with transitional cell carcinoma than other types of bladder cancer every year. Even though your cat may be urinating more often he may be passing very little urine each time due to possible blockage of the urinary tract by a bladder tumor.
Cats with bladder cancer may strain to defecate as well. A case of feline rectal prolapse which appeared to be secondary to transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is described. Symptoms of feline bladder cancer include bloody urine straining to urinate and increased frequency of urination.
Hematuria Hematuria stranguria pollakiuria are common presenting signs. Extension of the neoplasm beyond the bowel wall was found in 85 of dogs and 71 of cats at necropsy. Neoplasms of the ureters bladder and urethra are uncommon in dogs and rare in cats.
Epithelial most common or connective tissue. A bladder tumour is a benign or cancerous tumour of the bladder or urethra of cats. Clinical signs and ancillary testing.
Urinary bladder cancer however easily spreads to other areas of the body and may soon show the following symptoms. Symptoms of Bladder Cancer. Tumors location vary greatly inside the bladder.
The occurrence of bladder cancer is more common in female cats. The exact etiology is unknown. The urinary bladder is the most common site of lower urinary tract neoplasia in both dogs and cats 1 2.
Renal neoplasia is cancer located in the kidney. The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma. Most common tumor type.
Start studying Neoplasia of Urinary Tract. Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Lower Urinary Tract in Dogs. The diagnosis of a urinary bladder neoplasm is generally delayed because of a lack of overt clinical signs or a partial response to empirical treatment.
A urinary tract tumor is a type of cancer that develops from the disorganized uncontrolled growth of cells that make up the urinary system. Blood in the urine. 1 2 Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most prevalent lower urinary tract cancer in dogs and considerable information regarding TCC is available for dogs including common anatomical.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Renal Bladder and Urethra in Cats. The typical symptoms of bladder tumors include. The storage function of the bladder may allow for prolonged contact with carcinogens.
Hematuria stranguria dysuria pollakiuria are common presenting signs. The most common sites of metastases in the dog include the regional lymph nodes liver and lungs. Bladder neoplasia is rare in cats but is more common in cats older than 10 years.
Painful urination and the cat may be very vocal when urinating.
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis Vca Animal Hospitals

Transitional Cell Carcinoma In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Partner Vin

Bladder Tumor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease Flutd International Cat Care
Fibrosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder In A Cat
Bladder Cancer In Cats Innovet Pet

Vet Talk Liver Disease In Dogs And Cats Is Your Pet At Risk Liver Problems Diabetic Dog Benadryl For Cats

Neoplasia Of The Urinary System In Small Animals Urinary System Msd Veterinary Manual
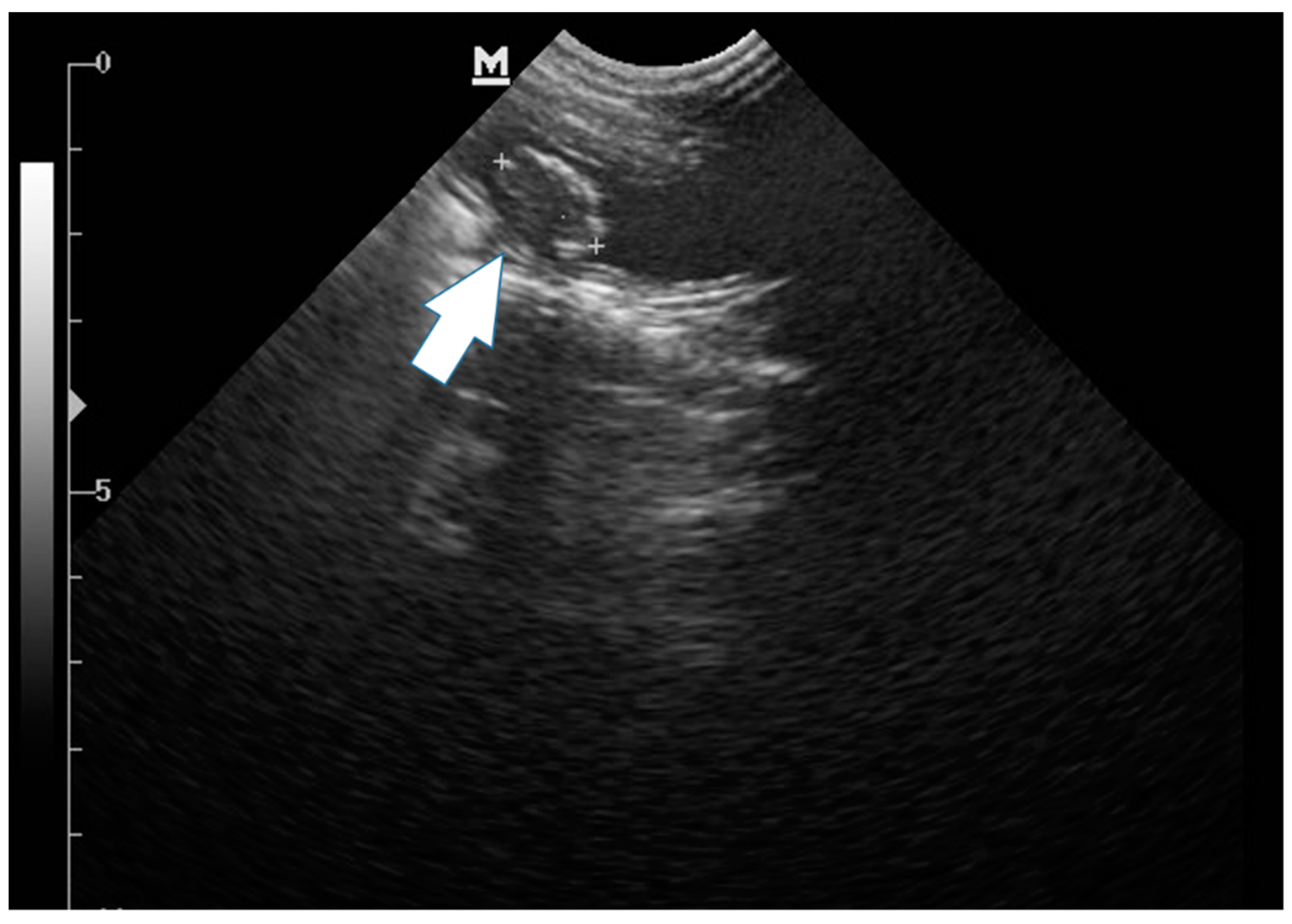
Veterinary Sciences Free Full Text Long Term Survival Of A Cat With Primary Leiomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder Html
Some Unusual Bladder Tumours In Dogs Vet Practice Support
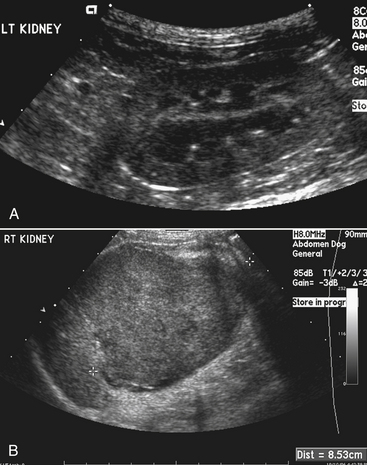
Tumors Of The Urinary System Veterian Key

Pdf In Situ Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of Urinary Bladder In A Cat Semantic Scholar

Pdf Treatment Of Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of Urinary Bladder Using Meloxicam In A Dog A Case Report Semantic Scholar
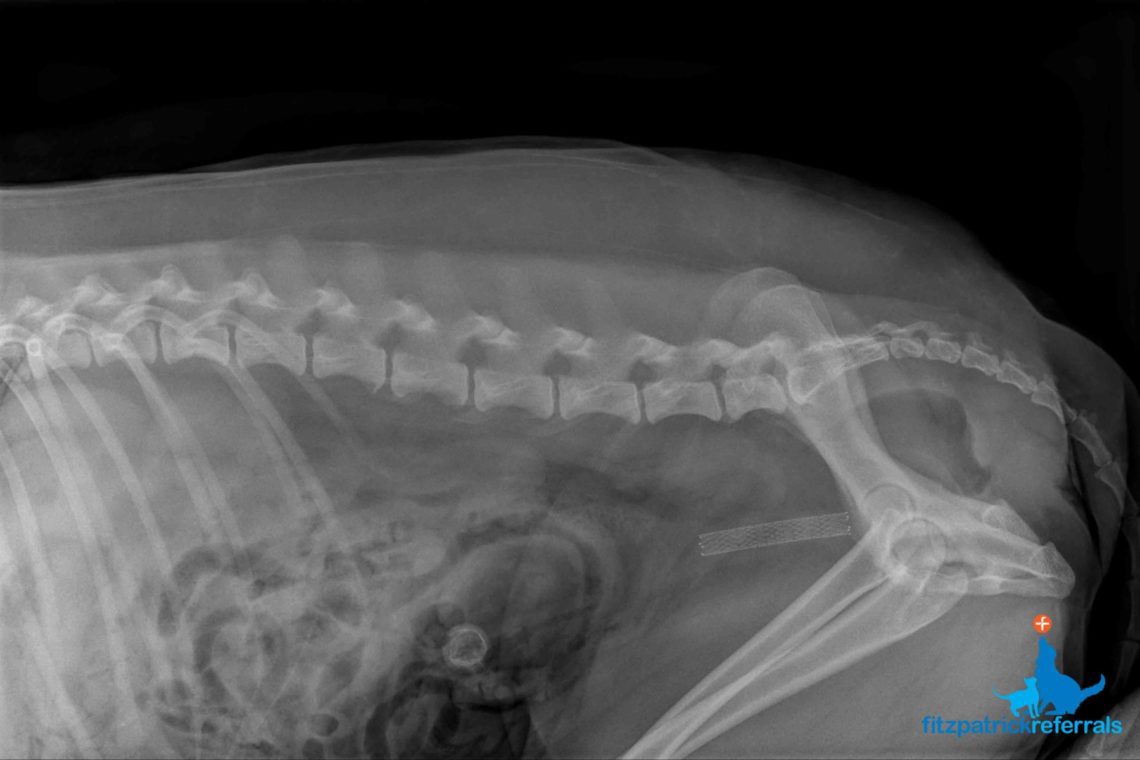
Urinary Cancer Fitzpatrick Referrals

Feline Kidney Anatomy Vet Tech Student Veterinary Tech Dog Anatomy

Urinary Tract Tumor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Urinary Bladder Cancer Research College Of Veterinary Medicine Purdue University